Historic and Modern British Art
Artist biography
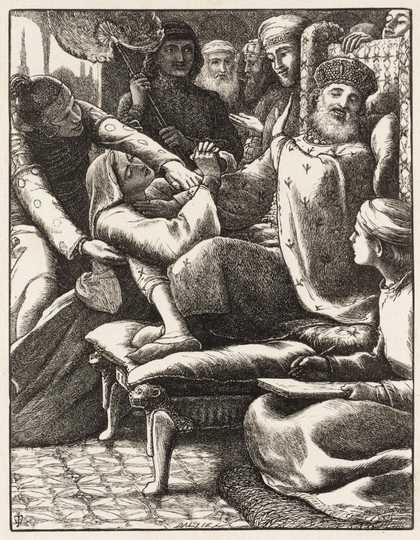
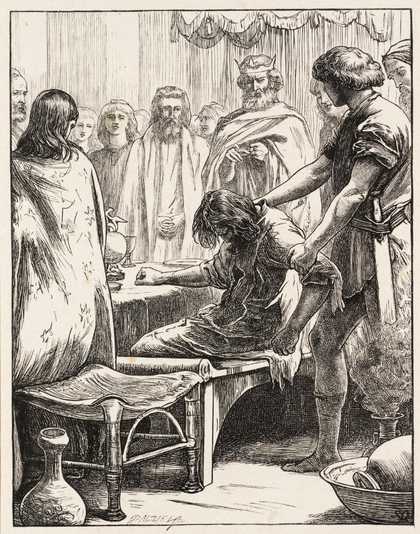
At the Royal Academy he became friendly with fellow student William Holman Hunt, and contributed with Hunt and Dante Gabriel Rossetti to the Cyclographic Society. In 1848 the three helped form the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood. His first Pre-Raphaelite painting was Isabella (1848-9, Walker Art Gallery, Liverpool), which he exhibited at the Royal Academy in 1849. His entry for the following year, Christ in the House of His Parents ('The Carpenter's Shop') (1849-50, Tate Gallery N03584), was received unfavourably.
In 1855 he married Effie Chalmers, Ruskin's former wife, with whom he had fallen in love while he was holidaying with the Ruskins in Scotland. The couple settled in Perth, where he painted Autumn Leaves (1855-6, City of Manchester Art Galleries).
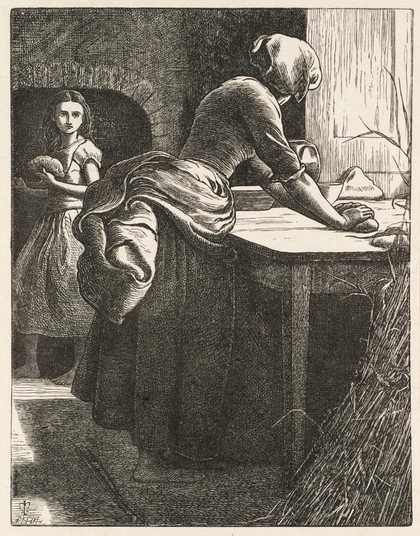
Between 1855 and 1864 Millais made illustrations for numerous publications, including the Moxon edition of Tennyson's poems (1857), the magazine Once a Week (1859 onwards) and several novels by Trollope. He moved back to London in 1861, where he achieved popular success as a painter of child subjects such as Bubbles (1886, A. & F. Pears Ltd.), which became famous as an advertisement for Pears soap. Also popular were his paintings of beautiful young women, such as Stella (1868, Manchester City Art Gallery). He built up a practice as a portraitist from the early 1870s, his sitters including Thomas Carlyle (1877), Lillie Langtry (1878), Gladstone (1879 and 1885), Disraeli (1881) and Tennyson (1881).
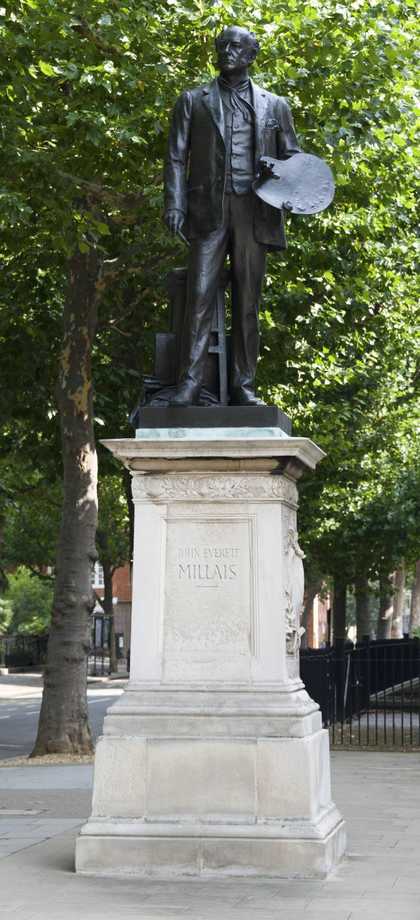
Millais was made an Associate of the Royal Academy in 1853, and a full member in 1863. In 1885 he was created a baronet and in 1896 was elected President of the Royal Academy, but died shortly thereafter in London. He is buried in St Paul's Cathedral.
Further reading:
John Guille Millais, The
Life and Letters of Sir John Everett Millais, 2 volumes, London 1899
Leslie Parris (ed.), The Pre-Raphaelites, exhibition catalogue, Tate Gallery, London 1984, reprinted 1994
Terry Riggs
January 1998
Wikipedia entry
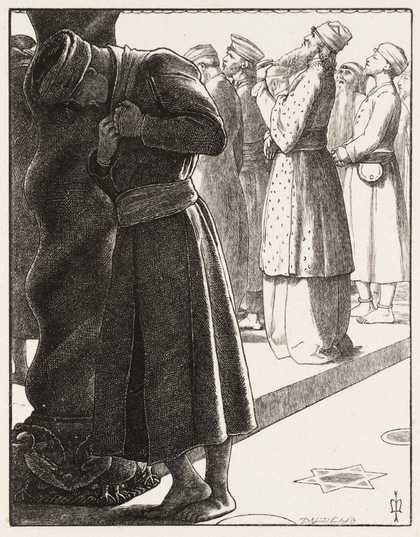
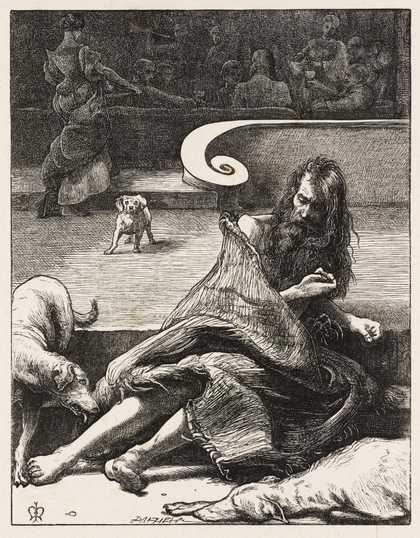
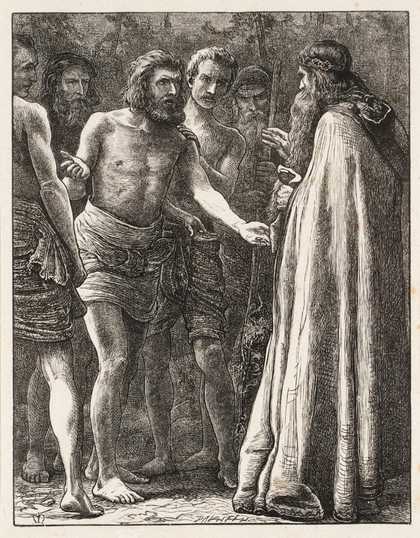
Sir John Everett Millais, 1st Baronet (UK: MIL-ay, US: mil-AY; 8 June 1829 – 13 August 1896) was an English painter and illustrator who was one of the founders of the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood. He was a child prodigy who, aged eleven, became the youngest student to enter the Royal Academy Schools. The Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood was founded at his family home in London, at 83 Gower Street (now number 7). Millais became the most famous exponent of the style, his painting Christ in the House of His Parents (1849–50) generating considerable controversy, and he produced a picture that could serve as the embodiment of the historical and naturalist focus of the group, Ophelia, in 1851–52.
By the mid-1850s, Millais was moving away from the Pre-Raphaelite style to develop a new form of realism in his art. His later works were enormously successful, making Millais one of the wealthiest artists of his day, but some former admirers including William Morris saw this as a sell-out (Millais notoriously allowed one of his paintings to be used for a sentimental soap advertisement). While these and early 20th-century critics, reading art through the lens of Modernism, viewed much of his later production as wanting, this perspective has changed in recent decades, as his later works have come to be seen in the context of wider changes and advanced tendencies in the broader late nineteenth-century art world, and can now be seen as predictive of the art world of the present.
Millais's personal life has also played a significant role in his reputation. His wife Effie was formerly married to the critic John Ruskin, who had supported Millais's early work. The annulment of the Ruskin marriage and Effie's subsequent marriage to Millais have sometimes been linked to his change of style, but she became a powerful promoter of his work and they worked in concert to secure commissions and expand their social and intellectual circles.
This biography is from Wikipedia under an Attribution-ShareAlike Creative Commons License. Spotted a problem? Let us know.
Read full Wikipedia entry